Polkadot Explained for Beginners : Solving Scalability and Interoperability

When it comes to the matter of Polkadot, whose native token is represented by DOT, it is simply not just another cryptocurrency like Bitcoin or Ethereum. Polkadot is a foundational technology that is aimed at connecting different cryptocurrencies together. Scalability and Interoperability are two main problems faced by the world of cryptocurrencies. Polkadot aims to solve both, and it is for this precise reason that it is called a ‘Layer 0’ meta protocol.
Let us imagine that the current cryptocurrency realm, which contains so many different coins and their blockchains, as different nations with their own language. Then, Polkadot is the universal translator for all these cryptocurrencies. This way, Polkadot enables seamless trade and communication between all blockchains, without compromising their security and integrity.
In this beginner’s guide, we will take a dive into the world of Polkadot, try to understand its core vision, how the unique architecture works, and how it is reshaping the future of the decentralized internet, which is commonly referred to as Web 3.0.
What Blockchain Problem Does Polkadot Solve?
To better understand what solutions Polkadot brings to the table, we must first understand what are the existing problems that act as a limiting factor in the current realm of blockchains.
Problem With Isolation
Most Blockchains exist as digital silos. In a normal scenario, it is impossible for Bitcoin to interact with Ethereum. Similarly, Ethereum is unable to communicate with a supply management blockchain built by some other corporation. What this lack of ability to communicate with each other translates into is that data or value cannot be moved between these networks. For users to make this communication possible, they have to rely on centralized exchanges and/or bridges, which puts security under threat.
This communication friction limits the potential for creating a truly decentralized ecosystem. Polkadot aims to eliminate or reduce this friction, allowing various blockchains to communicate with each other without the need for a trusted third-party intermediary.
The Dilemma Of Scalability
Blockchain technology operates under the constraint, which is called the “Blockchain Trilemma”. This basically means that a network can only optimize two of the three following properties.
Blockchain technology faces the ‘Blockchain Trilemma,’ meaning a network can optimize only two of the three key properties: decentralization, security, and scalability.
For instance, since its conception, Bitcoin and Ethereum have prioritized decentralization and security. This is why their transactions are often slow and costly. Polkadot addresses this issue by introducing a unique architecture that processes transactions in parallel. This vastly improves scalability while maintaining robust security.
Architecture of An Interconnected World
Polkadot’s architecture is highly innovative; it comprises three layers that enable it to achieve its goals. The Relay Chain, the Parachain, and the Bridges are the three layers that help Polkadot in achieving its goal of decentralization, security, and scalability.
The Relay Chain-The Central Nervous System
The primary blockchain is the Relay Chain. It is the heart that drives the operations that lead to the network’s shared security, consensus, and coordination. The relay chain can be thought of as the central governing body that enforces law and maintains defensive systems.
The Relay Chain does not handle complex application logic like a smart contract. Its job is simple but critical. The Relay Chain is what determines which transactions are valid across the entire ecosystem. The Relay Chain achieves this through a sophisticated consensus method known as the Nominated Proof of Stake (NPoS). Once the Relay Chain confirms a transaction, it is final and irreversible.
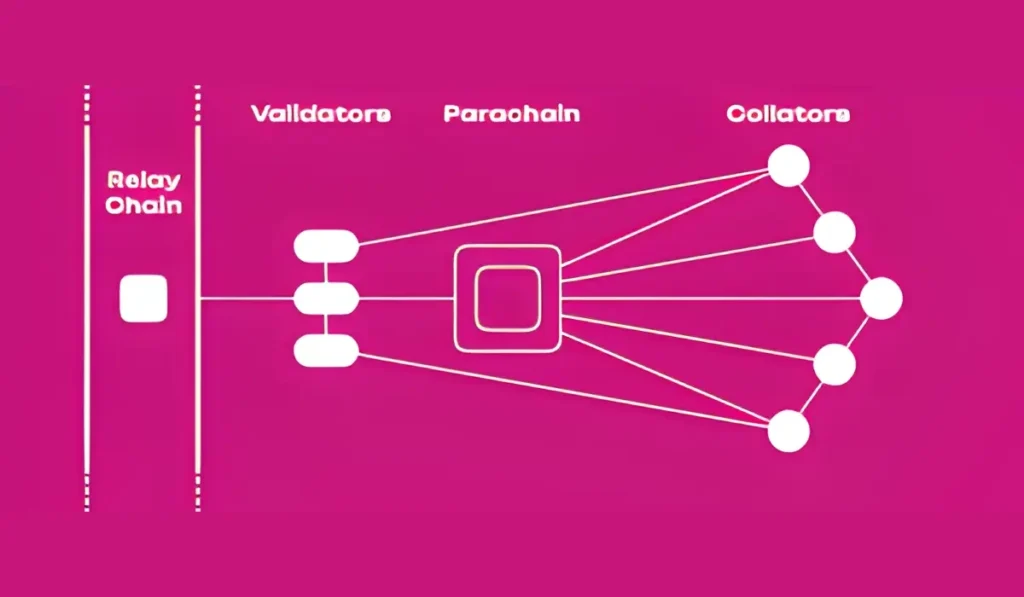
Since the Relay Chain has to do only one job, ensure security and coordination, it remains fast, efficient, and robust.
Parachains
Parachain is short for parallelized chains. These are sovereign blockchains that run alongside the Relay Chain. These parachains achieve their security by plugging themselves into the Relay Chain.
If we consider the Relay Chain as the Central government of a nation, then the Parachains are the states within that nation. Each parachain can have its own unique rules and governance models. Parachains feature tailored use cases. One parachain may be optimized for ultra-fast decentralized finance (DeFi), while another might be built for identity verification, and a third one could be built for Web 3.0 gaming.
This specialization is the key feature of Parachains. Instead of focusing every application onto a single congested blockchain, which was the case of Ethereum in the early days, Polkadot allows developers to build custom blockchains optimized for their specific needs. This enhances efficiency and reduces bottlenecks.
Bridges: Connecting Everything To The Outside World
Bridges are specialized parachains built to link the Polkadot ecosystem to external networks with their own independent security features that can prevent the weak points of other networks. It is these bridges that allow data flow in and out of the Polkadot system seamlessly.
Governance
The native asset of the Polkadot network is the DOT token. Unlike other coins that may often present no use cases, the DOT token has three main functions to perform they are governance, staking, and bonding.
Since Polkadot is a decentralized network designed to be owned by its users, there is a governance system in place. DOT holders are the governing body of the network. These members can propose network upgrades, vote on critical decisions, and decide how treasury funds are spent in the future. In essence, the DOT token gives its holder the opportunity to express their opinion regarding the future direction of the network.
Staking For Securing The Network
Polkadot makes use of the Nominated Proof of Stake or NPoS staking mechanism to ensure the security of the network. This staking process requires the participants to stake or lock up their tokens. The staking plays a crucial role in validating transactions and securing the network.
Staking in itself has two main roles: validators and nominators. Validators are the nodes that run the complex software that secures the Relay Chain, which is the central system of Polkadot. It is here that transactions are validated from parachains and new blocks are produced. Validators put a large amount of DOT in the lock-up and are heavily rewarded for their efforts in keeping the network secure.
Nominators are regular DOT holders; they do not have to run a full node; rather, they would nominate trustworthy validators. Their role is to support the validators, and they receive a share of the earnings.
Bonding-The Entry Fee For Parachains
For a project to launch its own parachain and enter the Relay Chain, it must go through a competitive auction process. The winning project must bond or lock up a substantial amount of DOT tokens for the duration of its lease, which is usually up to two years.
The bonding mechanism is put in place to ensure that the projects are financially committed and prevent spam or malicious actors from clogging up the system. When the lease expires, the bonded DOT is returned to the project or the community members who contributed it to the auction bid in the first place.
Conclusion
Web 3.0 is the vision for the next generation of the internet. A decentralized internet built on an open, trustless network is going to trump concentrated centralized networks that are run on corporate servers. Polkadot has the technology to serve as the key foundation for this in principle. Polkadot has easily solved the fragmentation issue that has been holding Web 3.0 back. By enabling true interoperability and scalability, Polkadot allows a complex ecosystem of specialized blockchains to coexist and interact seamlessly.
It is an ambitious project that is aimed at creating a digital future where assets and information can flow freely across diverse blockchain platforms. This free flow is not hindered by security issues, as everything is coordinated by one highly secure decentralized protocol.
FAQs
Polkadot is a Layer 0 blockchain platform that connects multiple blockchains, enabling secure communication and interoperability.
It links independent blockchains so that they can share data and value without relying on centralized bridges or exchanges.
Polkadot processes transactions in parallel through parachains, which reduces congestion and increases transaction speed, making it highly scalable.
Parachains are specialized independent blockchains connected to Polkadot’s Relay Chain, each optimized for unique use cases.
DOT is used for three main things from the network perspective. It is used for governance, staking for security, and bonding to launch parachains.
Crypto & Blockchain Expert

