It can be considered a mad enthusiast’s fever dream that one day Bitcoin will reach a value of $1 billion per coin. Even though the idea seems like a good investment opportunity, we will discuss in this article why Bitcoin can’t reach that valuation.
Practical Barriers to Bitcoin Reaching $1 Billion
For an asset to be worth $1 billion, that asset should replace every single monetary asset on this planet. Comparing the use cases of Bitcoin to those of other assets, it is doubtful that Bitcoin will replace them all. Becoming a reserve currency is a tough challenge; there are three critical functions that any currency intending to acquire the status of a reserve currency must satisfy:
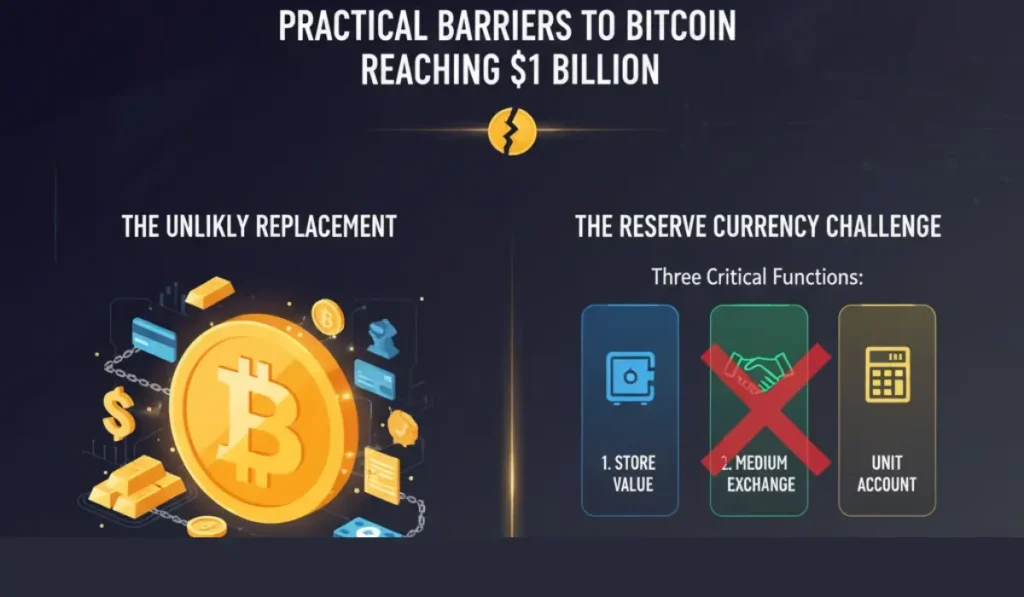
- It must be a store of value
- It must be a medium of exchange
- It must be a unit of account
At the moment, Bitcoin does not meet all three requirements, and it is still unlikely that even if Bitcoin were to attain all the necessary status and support to be a reserve currency, or even if it were to become the reserve currency that its price would climb to 1 billion dollars per coin.
Financial Constraints To Reach The $1 Billion Mark
By market capitalization math, Bitcoin can never reach the $1 billion mark. With a total supply of 21 million Bitcoins, the asset is at a fixed supply. No more coins can be mined, nor can the mined coins be destroyed.
With the supply of the asset being fixed, let us do some simple math. We will multiply the total supply by the expected price of $1 billion and see where the market capitalization stands.
21 million coins x 1,000,000,000 = 21 quadrillion
A total market capitalization of 21 quadrillion is a value much higher than the estimated global wealth and the global GDP. In fact, it is 200 times the estimated global wealth and 100 times the global GDP as of now.
A single asset surpassing the global GDP by 100 times is practically impossible. How valuable an asset is it cannot exceed the global GDP and wealth values.
Values Stabilizing Due to Use Cases
Bitcoin was once promised to be the holy grail that would replace all currencies of the world through a decentralized system. Now, however, the highest application of Bitcoin is that it is a store of value.
But even though Bitcoin is a store of value, the highly volatile nature of Bitcoin’s price is a matter of concern for all investors. This has largely questioned the credibility of the world’s first cryptocurrency.
Another aspect that potentially prevents the price from reaching such highs is the lack of chances for practical adoption. There are two main reasons why Bitcoin would be hard to adopt as a currency that is going to replace traditional fiat currencies.
- High transaction costs
- Volatile Prices
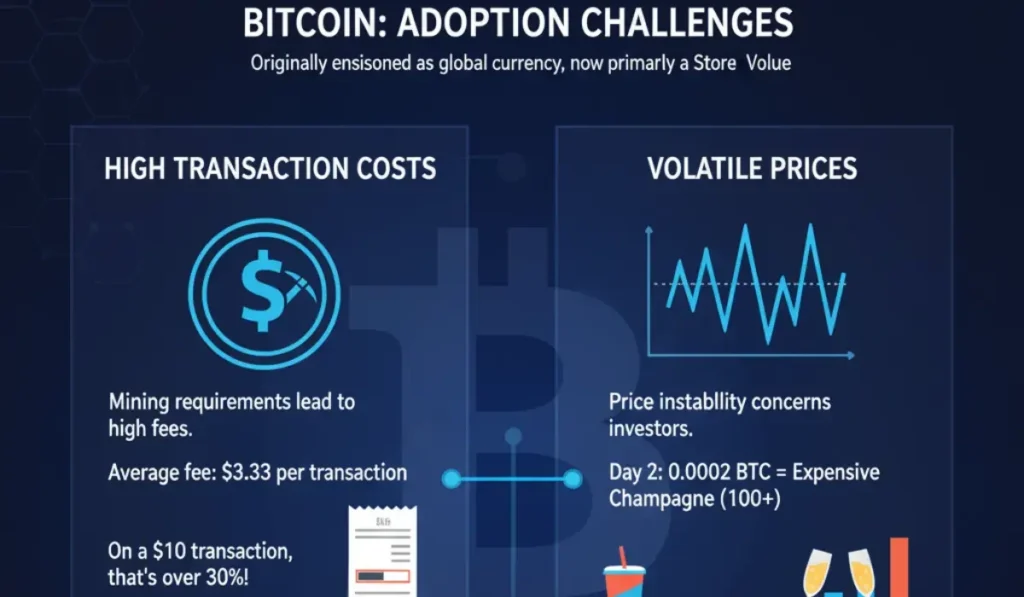
High Transaction Costs
Bitcoin often has high transaction costs courtesy of the harder mining requirements posed by the blockchain. For instance, a transaction cost of $3.33 applies per transaction as of the writing of this article.
The world’s most common form of fiat transaction is microtransactions; millions of microtransactions are performed every day throughout the world. To facilitate the blockchain’s optimum performance, collecting transaction fees is a necessity, but a $3.33 transaction charge on an average transaction of $10 is a steep fee, calculated to over 30% of the original transaction’s value.
Even though Bitcoin Lightning Networks can be used to stabilize the fees and reduce them, they are still rather complicated to use with the invoicing system.
Since transactions require a specific technological setup, this incurs additional costs to the commercial setup as well.
Volatile Prices
From what can be understood about Bitcoin’s price so far, it can be confidently stated that Bitcoin is an asset with a highly volatile price. If we compare our earlier example of an average $10 spend, we can see that the value of this much bitcoin on one day may buy you a soft drink, and if the prices go high, it may buy you the most expensive champagne the very next day.
This level of uncertainty is not an ideal characteristic of a currency. Having your entire month’s salary valued at a day’s salary in a week’s notice is unacceptable, but that could happen if a volatile currency replaces the traditional, stable fiat.
Conclusion
The chances of Bitcoin reaching a value of $1 billion are theoretically impossible, as we saw through the calculations. Additionally, we were able to see how Bitcoin would never achieve such a high valuation since it cannot replace a traditional fiat as the global reserve currency for reasons like transaction costs and volatile prices.
It does not mean that Bitcoin has no future, just that an absurd valuation, which is often a topic of heated debate on forums and fan pages, is nothing but pointless efforts to glorify an already reputable asset.
FAQs
This value or the fixed supply limit is built into the protocol of Bitcoin, hence there cannot be more than 21 million Bitcoins in total.
The world GDP is calculated as the total value of all finished goods and services in a year; hence, all assets are a part of the GDP, and hence an asset’s price cannot be higher than that of the world GDP.
At the current rate of inflation, it would take at least 462 years for a dollar’s worth of purchasing power to cost $1 billion. This is calculated by projecting upwards the current rate of inflation; in a real-life scenario, inflation rates would fluctuate.
They are costly for two reasons: the value of bitcoin and the difficulty in processing a block of transactions. Since the block reward is calculated in bitcoins, the higher the price of Bitcoin, the higher the transaction fees appear to be.
Since Bitcoin’s supply is capped at 21 million coins, it is a deflationary asset. Hence, demand has a huge role in determining the price. This can cause prices to swing occasionally, making Bitcoin’s price highly volatile.

